Volume 43 Number 3
Around the WCET® world
Samantha Holloway
For referencing World Council of Enterostomal Therapists®. Around the WCET® world. WCET® Journal 2023;43(3):10.
Embedding the International Skin Tear Advisory Panel’s Skin Tear Classification into practice
The International Skin Tear Advisory Panel (ISTAP) developed a classification system for skin tears in 20111. Following this a study was undertaken to establish the validity of the system in clinical practice2. This study showed that the ISTAP classification was easy to use for practitioners in different clinical settings and also in different countries. Subsequently a larger validation study was carried out in 2019 across 44 countries and involving 1601 participants3. The conclusion of this research was that the classification system is supported by evidence for validity and reliability, with the recommendation that this should be the system of choice for the systematic assessment and reporting of skin tears in clinical practice and research globally.
The ISTAP Skin Tear Classification System categorises skin tears into Types, with Type 1 being a linear or flap skin tear with no tissue loss, Type 2 involves partial flap loss (where the flap cannot be repositioned to cover the wound bed) and Type 3 indicates complete flap loss (Figure 1).
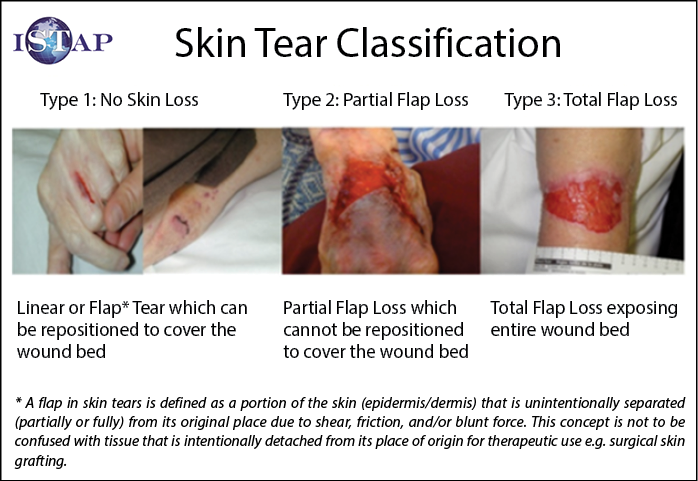
Figure 1 ISTAP Skin Tear Classification System
The first aid measures to follow when a skin tear does occur is to, first, stop the bleeding and then, gently cleanse the wound to remove any debris. If a skin flap is present this should be reapproximated to cover the wound bed and then the skin tear should be classified using the ISTAP Skin Tear Classification System4.
The classification system is now available in 14 other languages other than English, being Arabic, Czech, Dutch, French, Hebrew, Japanese, Spanish, Chinese, Danish, German, Italian, Portuguese, Swedish and Turkish (skintears.org). ISTAP has had the pleasure of supporting and working with colleagues in these countries to aid in the translation process and advise on implementation.
The next steps in developing the ISTAP classification system is to ensure it is validated in different populations with different skin tones as we recognise that the current system reflects how skin tears appear in predominantly white Caucasian skin. This is where ISTAP needs your help! We would welcome opportunities to collaborate with colleagues to create a repository of images of skin tears in different skin tones. We would also encourage anyone seeking to validate the ISTAP classification in different populations, particularly in groups with different skin tones, to contact us (info@skintears.org) for support with this.
WCET®的相关内容
Samantha Holloway
将国际皮肤撕裂伤专家咨询组的皮肤撕裂伤分类付诸实践
国际皮肤撕裂伤专家咨询组(ISTAP)于2011年制定了皮肤撕裂伤分类系统1。随后进行了一项研究,以确定该系统在临床实践中的有效性2。这项研究表明,ISTAP分类便于不同临床环境以及不同国家的执业医师使用。随后,还于2019年在44个国家进行了一项规模更大的验证研究,纳入了1601例参与者3。这项研究得出结论,该分类系统的有效性和可靠性得到了证据支持,并建议将其作为全球临床实践和研究中皮肤撕裂伤系统评估和报告的首选系统。
ISTAP皮肤撕裂伤分类系统将皮肤撕裂分为以下几类:1类为无组织损失的线性或皮瓣皮肤撕裂伤,2类为部分皮瓣损失(皮瓣无法重新定位覆盖伤口床),3类为完全皮瓣损失(图1)。

图1 ISTAP皮肤撕裂伤分类系统
出现皮肤撕裂伤时,首先应采取的急救措施是止血,然后轻轻清洁伤口以清除任何碎屑。如果存在皮瓣,应重新对位以覆盖伤口,然后使用ISTAP皮肤撕裂伤分类系统对皮肤撕裂伤进行分类4。
目前,该分类系统有除英语外的其他14种语言版本可用,包括阿拉伯语、捷克语、荷兰语、法语、希伯来语、日语、西班牙语、中文、丹麦语、徳语、意大利语、葡萄牙语、瑞典语和土耳其语(skintears.org)。ISTAP很高兴能够为这些国家的同事提供支持并与他们合作,协助完成翻译工作,并就其执行情况提出建议。
我们认识到,当前系统反映了大多数高加索人皮肤出现皮肤撕裂伤的情况,因此开发ISTAP分类系统的下一步工作是确保在各类不同肤色的人群中对其进行验证。ISTAP希望您提供相关帮助!我们期待有机会与同事合作,创建不同肤色皮肤撕裂伤图像的资料库。同时,我们还鼓励想要在不同人群(特别是具有不同肤色的小组)中对ISTAP分类进行验证的人员与我们联系(info@skintears.org),以获得相关支持。
Author(s)
Samantha Holloway
ISTAP President
References
- LeBlanc K, et al. (2011) Skin Tears – State of the Science: Consensus Statements for the Prevention, Prediction, Assessment, and Treatment of Skin Tears Advances in Skin & Wound Care. 24(9): 2-15.
- LeBlanc K, Baranoski S, Holloway S, Langemo D. Validation of a new classification system for skin tears. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2013 Jun;26(6):263-5. doi: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000430393.04763.c7. PMID: 23685526.
- Van Tiggelen H. et al. (2019), Standardizing the classification of skin tears: validity and reliability testing of the International Skin Tear Advisory Panel Classification System in 44 countries. Br J Dermatol. doi:10.1111/bjd.18604
- Holloway S & LeBlanc K. Reapproximating a Skin Tear Flap. Advances in Skin & Wound Care 35(8):p 462-463, August 2022. | DOI: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000835124.90642.ce


